Dictionary

Ceramics
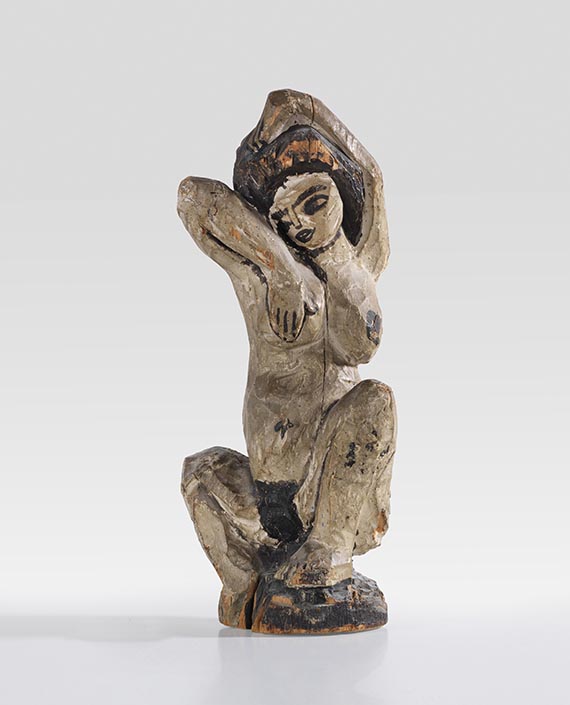
Ceramics (Greek: "keramos"] is the generic term for pottery and the durable products made from fired clay. Pottery making is one of man's oldest cultural achievements. The earliest pottery finds date from the Middle Stone Age. Ceramics have manifold uses, as building material, for storing provisions and at the same time for the creation of art works. Ceramics are classified as either coarse or fine. Coarse ceramics include tiles and roofing tiles, pipes, etc. Fine ceramics include vessels, tableware, decorative wares and art objects. Water is added to soft clay at room temperature, then the clay is allowed to dry. When completely dry, the piece is fired at very high temperatures. The fired clay body is porous and absorbs moisture. This property is dealt with by glazing the body. Glazing is, of course, also used as decoration. The porosity of ceramics can also be influenced by sintering the bodyif it is mixed with suitable fluxes. Faience (maiolica), porcelain, lead-glazed earthenware, stoneware and terracotta are subsumed under the generic term ceramics.
Ceramics (Greek: "keramos"] is the generic term for pottery and the durable products made from fired clay. Pottery making is one of man's oldest cultural achievements. The earliest pottery finds date from the Middle Stone Age. Ceramics have manifold uses, as building material, for storing provisions and at the same time for the creation of art works. Ceramics are classified as either coarse or fine. Coarse ceramics include tiles and roofing tiles, pipes, etc. Fine ceramics include vessels, tableware, decorative wares and art objects. Water is added to soft clay at room temperature, then the clay is allowed to dry. When completely dry, the piece is fired at very high temperatures. The fired clay body is porous and absorbs moisture. This property is dealt with by glazing the body. Glazing is, of course, also used as decoration. The porosity of ceramics can also be influenced by sintering the bodyif it is mixed with suitable fluxes. Faience (maiolica), porcelain, lead-glazed earthenware, stoneware and terracotta are subsumed under the generic term ceramics.
Offers
Headquarters
Joseph-Wild-Str. 18
81829 Munich
Phone: +49 89 55 244-0
Fax: +49 89 55 244-177
info@kettererkunst.de
Louisa von Saucken / Undine Schleifer
Holstenwall 5
20355 Hamburg
Phone: +49 40 37 49 61-0
Fax: +49 40 37 49 61-66
infohamburg@kettererkunst.de
Dr. Simone Wiechers / Nane Schlage
Fasanenstr. 70
10719 Berlin
Phone: +49 30 88 67 53-63
Fax: +49 30 88 67 56-43
infoberlin@kettererkunst.de
Cordula Lichtenberg
Gertrudenstraße 24-28
50667 Cologne
Phone: +49 221 510 908-15
infokoeln@kettererkunst.de
Hessen
Rhineland-Palatinate
Miriam Heß
Phone: +49 62 21 58 80-038
Fax: +49 62 21 58 80-595
infoheidelberg@kettererkunst.de
We will inform you in time.